The radiology department is a vital part of the hospital. This is where a variety of tests are conducted to help physicians in other departments make an accurate diagnosis for different illnesses and follow-up on the changes in the patient’s condition, thus facilitating the process of choosing the right treatment course, whether through medications or surgery.
This unit contains the latest devices for conducting radiology tests with a high level of accuracy. These tests include:
– Bone examinations for all body parts, from the skull to the hands and feet, and the diagnosis of different fractures, infections, tumors, congenital deformities, and bone diseases associated with a lot of other diseases such as hereditary anemia, vitamin D deficiency, osteoporosis, rickets, etc… In addition to measuring children’s bone age.
– Joint tests for all body parts, X-rays are considered one of the main tests in assessing the condition of the joints and diagnosing accident-related injuries and various diseases that affect the joints, such as arthiritis, infections, congenital anomalies, and others.
– Spine examinations, they’re considered an integral part of spinal MRI examinations.
– Chest and lung examinations, they’re the main tests in diagnosing respiratory disorders.
– Abdomen examinations, which are used in the diagnosis of acute abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction, and gastrointestinal perforation, they’re also considered the main tests in diagnosing renal and bladder stones.
– Soft tissue examinations, they’re used to diagnose calcifications before performing more advanced and accurate examinations.
– Sinus examinations.

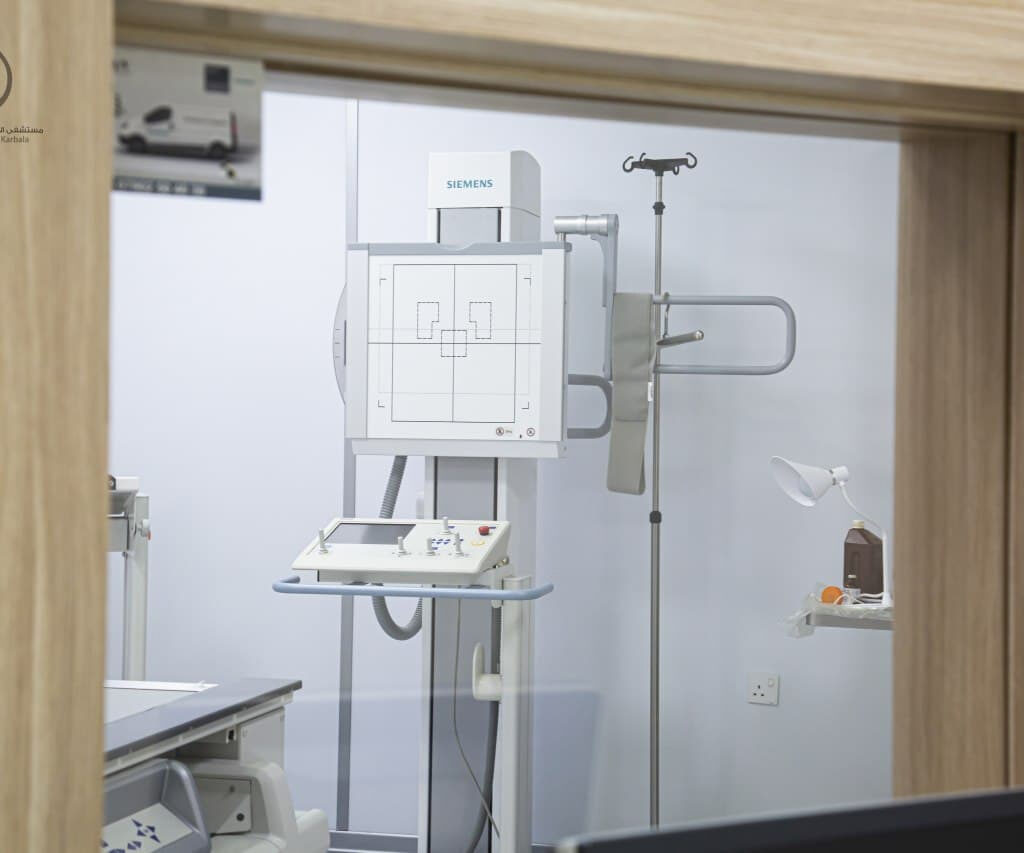
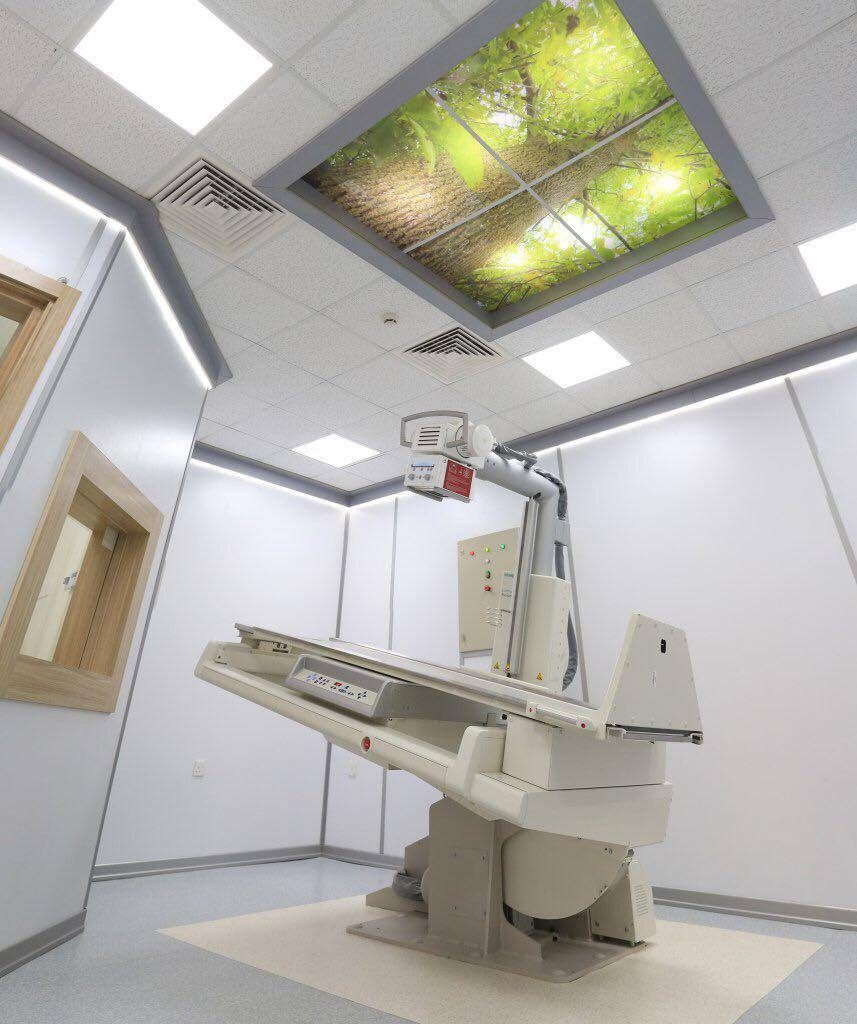
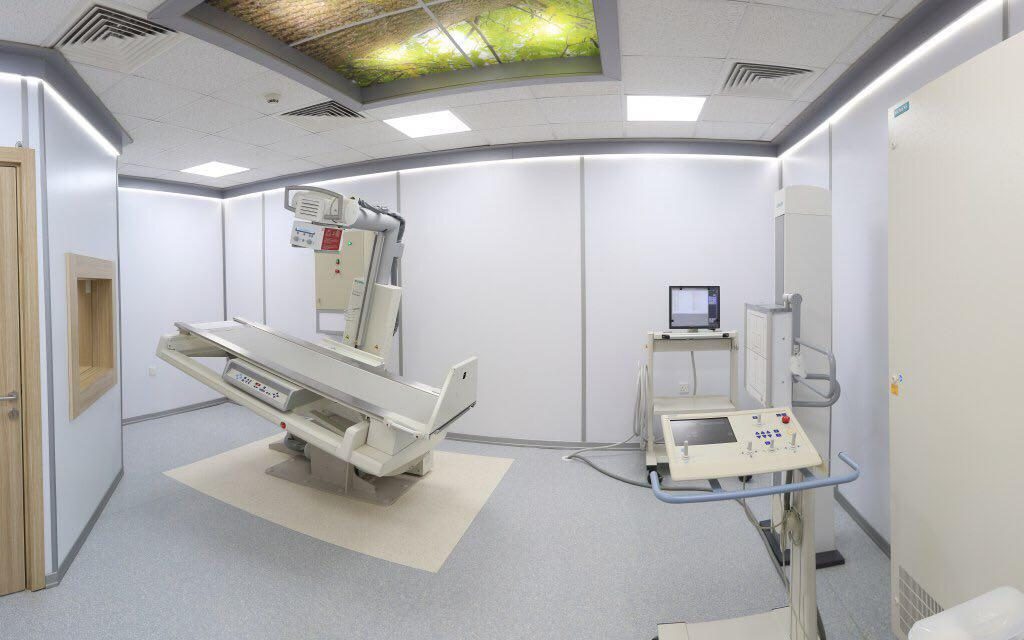
This unit contains the latest digital fluoroscope for radiographs of different body parts during movement in real-time, such as:
– Imaging of the movement of joints to measure the extent of movement limitation.
– Contrast radiography of the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine (colon), this is one of the important tests to observe the movement of food through the esophagus and determine the presence of partial obstruction, its type, and sometimes its cause. These tests are complementary to endoscopic examinations.
– Contrast radiography of the kidneys and urinary tracts in order to diagnose renal secretions, congenital anomalies, and ureteral obstruction.
– Contrast radiography of the bladder and urethra in order to diagnose various diseases.
– Contrast radiography of the uterus and ovarian tubes to determine any obstructions and the shape of the uterus.
– Contrast radiography of fistula to determine its depth and attachment to the viscera.
– The precise tests that are performed after certain surgeries to detect possible complications.
– Interventional procedures such as biopsies of histopathology of bones, breast, lungs, kidneys, lymph nodes, thyroid gland, and other tissues, as well as diagnostic interventions for bile ducts and urinary tracts, and treatment interventions such as guided biliary drainage and nephrostomy, catheter-guided drainage of fluids, and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
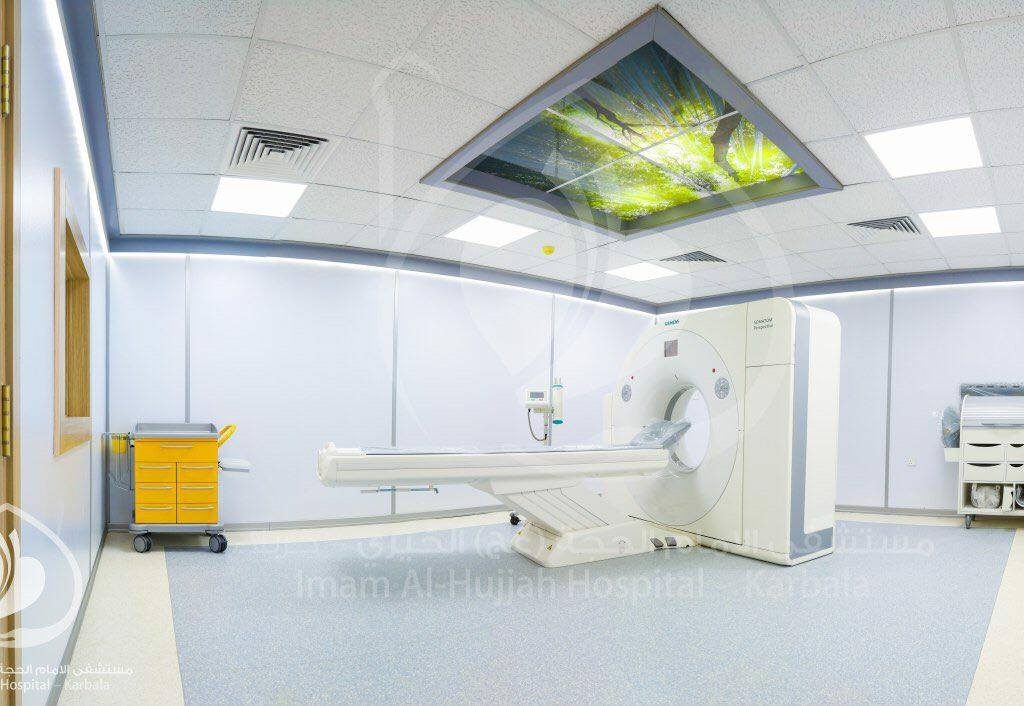
This unit contains a modern (64-chip) CT scanner with high accuracy and ability to diagnose many diseases that were difficult to determine before this type of examination was discovered. Some of the tests conducted by this device include:
– Primary test for stroke. Distinguishing stroke from a brain hemorrhage, because their treatment differs greatly.
– Accident examinations: Diagnosis of fractures and dislocations with great accuracy and speed for different body parts, and diagnosis of other injuries associated with bone and joint trauma, such as pneumothorax and pleural effusion.
– Basic examination for lung and airway disorders and injuries. The importance of this test became apparent recently in the diagnosis of COVID-19, especially when swab coronavirus tests aren’t avaialble.
– The most accurate test in the diagnosis of renal and ureteral stones, and determining their hardness and suitability for fragmentation.
– The precise tests for disorders of the digestive system.
– Determining the location, size, and spread of tumors, and following up on their response to treatment.
– Basic examination for sinus and ear disorders.
– Non-cardiac, cardiac vscular, and spinal cord examinations. – Quantitative CT studies and other CT-guided interventional procedures for different diseases.
Keep in mind that the patient who intends on getting a contrast CT scan must first undergo kidney test.
This unit contains a high-precision, advanced closed MRI machine (T1.5), and it’s used in performing a significant number of important tests which weren’t possible before this device was invented, such as:
– Diagnosis of nervous system and vertebrae disorders. MRI is considered one of the most important tests for brain and spinal cord diseases, such as genetic disorders, and diseases of the white matter, tumors, arterial and venous diseases. It’s also an essential test for the diagnosis of spinal disc herniation and following-up on the patient’s condition after undergoing surgery.
– Tests for bile ducts and renal disorders.
– Tests for disorders of the uterus, ovaries, congenital anomalies, tumors, fibrosis, ovarian cysts, and others.
– Tests to identify diseases and injuries of joints, tendons, and various infections, and post-joint replacement tests.
– Tests for rectum and bladder disorders and tumors.
– Eye socket examinations.
– Salivary gland examinations.
– Soft tissue examinations.
This type of radiography does not emit any ionizing radiation. It relies on the magnetic field, therefore, it’s affected by the presence of metal. The MRI technician must be informed about any existing shrapnel or implants, such as a pacemaker, and any previous surgery. Note that most modern implants do not interfere with the work of the MRI machine.
If the patient has a platinum implant, shrapnel, artificial joint, spine surgery, cochlear implant, heart
mesh, cardiac pacemaker, or any other metal, he must inform the receptionist before
reservation, and then inform the MRI technician and doctor.
– Undergo renal examination before undergoing contrast MRI.
– Attend half an hour before the test appointment. In some urgent cases, the appointment may be delayed
for 30 – 40 minutes.
– Bring any previous examination reports (X-rays, MRI, CT Scan, Ultrasound).
– In examinations that require fasting (such as bile duct, liver,
and abdominal tests) the receptionist must inform the patient prior to reservation.
– Test results are delivered after 24 – 48 hours, except during an emergency. The radiologist decides
if the patient was in an urgent condition.
– In case of postponing the appointment, please call the radiology department at 07723530119.
– If any of the above instructions are not clear, please return to the receptionist.
5. Ultrasound Scanning Unit: This unit contains the latest ultrasound and color doppler device. Ultrasound tests are very common and they determine the need for additional examinations to diagnose the disorder. These tests include:
– Initial examinations for acute abdominal pain, especially if appendicitis is suspected.
– Examinations of kidney, ureter, bladder, and prostate disorders.
– Main examination for pregnancy during all stages, and ovarian examination.
– Neck examinations, especially for the thyroid, salivary, and lymph glands.
– Color doppler for arteries and veins to diagnose obstructions, thrombosis, etc.
جميع الحقوق محفوظة لمستشفى الامام الحجة (عج) الخيري © 2023