Liver tumors are among the most common tumors due to the widespread occurrence of cirrhosis resulting from the B and C virus, which causes chronic hepatitis C, which in turn leads to cirrhosis.
Treatment of liver tumors:
– Surgical treatment by removing the tumor or liver transplantation, but this treatment is only suitable for a small category of patients.
– Modern non-surgical treatment using interventional radiology, which is the safest, most successful and most appropriate for most cases of liver patients.
Non-surgical treatment depends on various techniques, including:
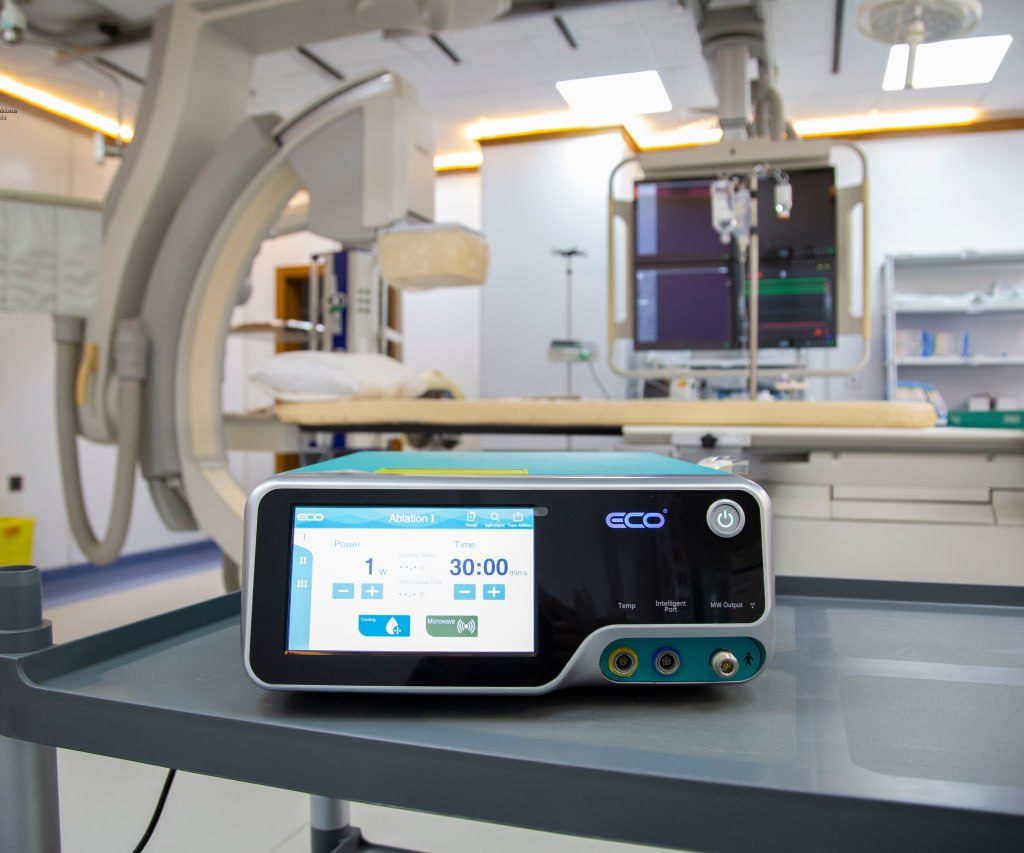
1) Cauterization of the tumor with thermal frequency or microwave:
A small needle is inserted into the site of the tumor under the influence of anesthesia and then it is eliminated with thermal cauterization.
2) Arterial injection via catheter:
Chemotherapy is injected through a fine catheter that enters the site of the tumor from a small opening in the upper thigh to the artery feeding the tumor.
3) Injection of a radioactive substance through a catheter:
This is the latest technology for treating liver tumors and relies on the injection of the radioactive substance yttrium. It is used in cases of liver tumors in which the tumor extends to the branches of the portal vein. These are fine granules of radioactive material that are concentrated in the location of the tumor and they destroyed it internally by radiation.
The patient can leave the hospital on the same day and continue his life normally after a very short recovery period.
– – Dr. Adnan Muhammad Jaber Al-Zaidi (specialization in diagnostic and interventional radiology and catheterization of the body and brain arteries, fellow of the Iranian University of Science)