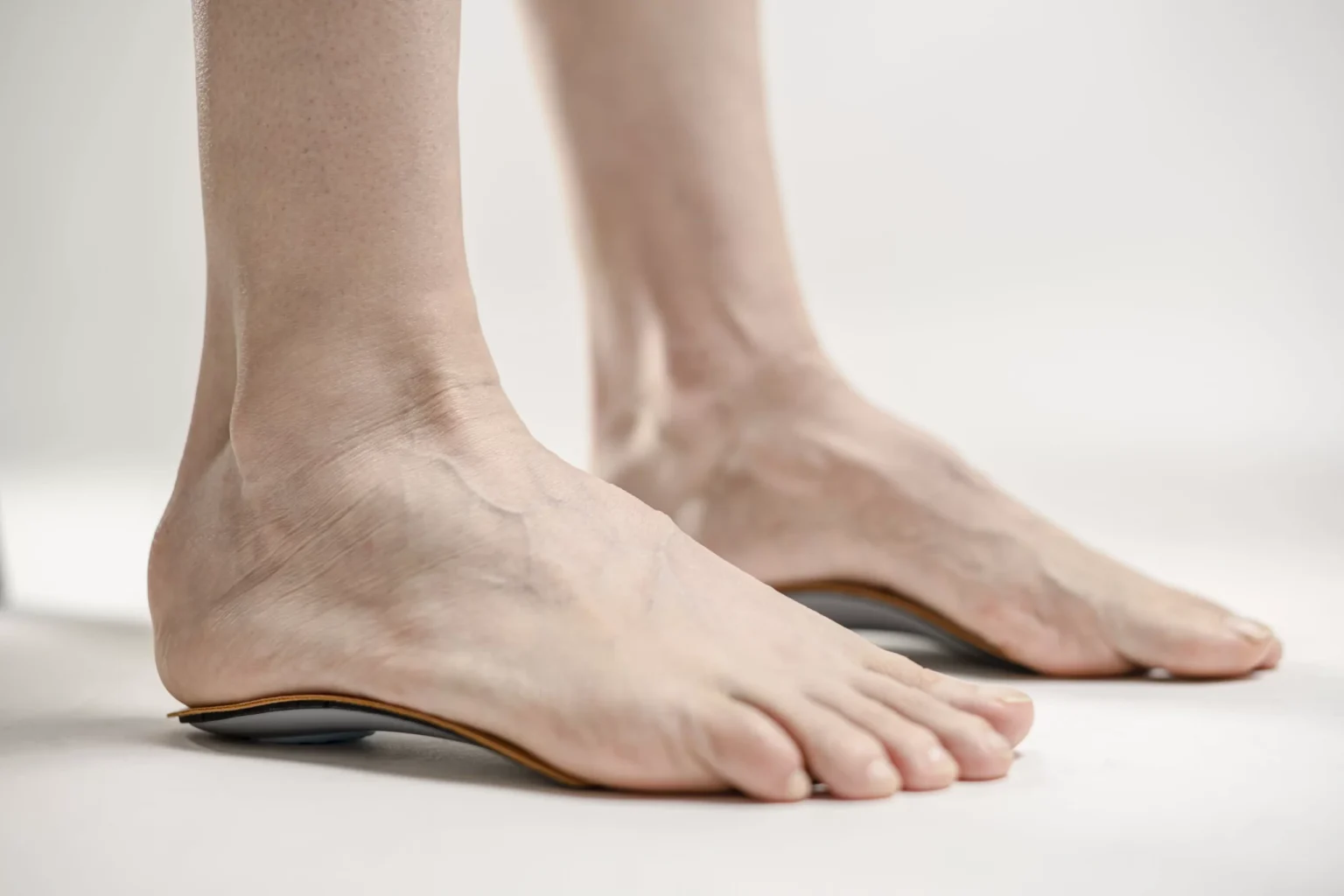
Flatfoot is a condition where the arch in the middle part of the inner side of the foot is lower than usual, while a typical foot arch is generally elevated above the ground.
Causes:
• Failure of the foot arches to develop properly during childhood; children are often born with flat feet, which typically develop arches by age six as the foot becomes less flexible. Around 1 or 2 out of every 10 children may retain flat feet into adulthood.
• Certain specific conditions, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Marfan syndrome.
• Tear or weakness in foot tendons due to injury, aging, or weight gain.
• More severe causes include foot or ankle injuries, ligament injuries in the foot, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.
Symptoms:
Flatfoot affects the alignment of the feet and legs and their functioning during movement. Symptoms may include consistent pain in the feet or legs, frequent tripping or falling, especially in children, or weakness, numbness, or stiffness in the feet, which may indicate flatfoot. Additional symptoms include:
• Pain in the heel, arch, leg, or other body parts.
• Pain along the posterior tibial tendon, located inside the foot and ankle, which may be accompanied by swelling on the inner ankle.
• Worsening pain with activity, where high-intensity or impact activities (like running) can be challenging, and some may struggle to walk or even stand for extended periods.
You should see a doctor if you experience foot pain, stiffness, weakness, or numbness or if you have problems with walking or balance.
Diagnosis: The diagnosis involves a CT scan to examine the bones of the foot, an MRI to examine the tendons, X-rays of the foot, and blood tests to check for arthritis.
Treatment:
If flatfoot does not cause pain or other concerns, treatment may not be necessary. However, if symptoms are present, treatment may include orthotics (such as arch supports that can help manage pain or issues related to flatfoot), stretching exercises for calf muscles to improve flexibility, and, rarely, flatfoot surgery.
Dr. Wissam Al-Taei
Rheumatologist