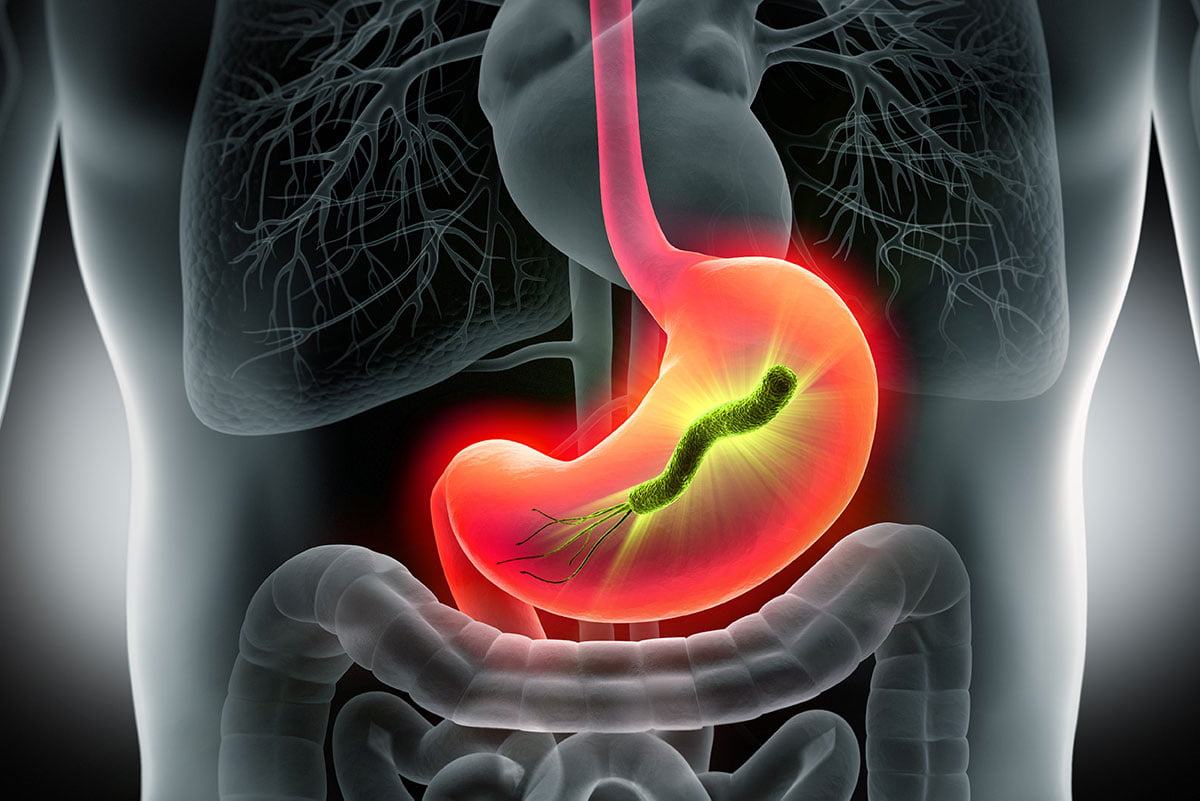
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that resides in the stomach and duodenum, causing infections in the affected person. It can also lead to diseases such as stomach ulcers and, if not treated promptly, may develop into stomach cancer.
Symptoms: A sharp and bothersome pain, increased acidity in the body to an unbearable level, acid reaching the mouth, acid reflux due to the bacteria, which makes your stomach reject food, loss of appetite and weight, frequent burping, stomach inflammations like severe bloating accompanied by diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting (in severe cases, dizziness or fainting, shortness of breath, and pale skin in severe conditions).
Diagnosis: When you visit the doctor, they will ask you to undergo a stool examination to detect any gastrointestinal diseases, as well as a Urea Breath Test. In this test, the patient drinks a special liquid containing urea, nitrogen, and radioactive carbon. The patient’s inhalation and exhalation are then tested using a plastic bag; if the person is infected with H. pylori, the breath composition will change. An endoscopy may also be done to confirm the presence of the bacteria in the stomach.
Prevention Methods:
- Wash your hands after using the bathroom and before eating.
- Do not eat undercooked food.
- Eat whole grains rich in fiber to aid digestion.
- Consume foods rich in Omega-3, such as fish, as well as ginger and garlic, to strengthen your stomach and immune system.
- Avoid smoking during this period.
Dr. Emad Geddoa