Dr. Hussein Hayder Al-Kurdi
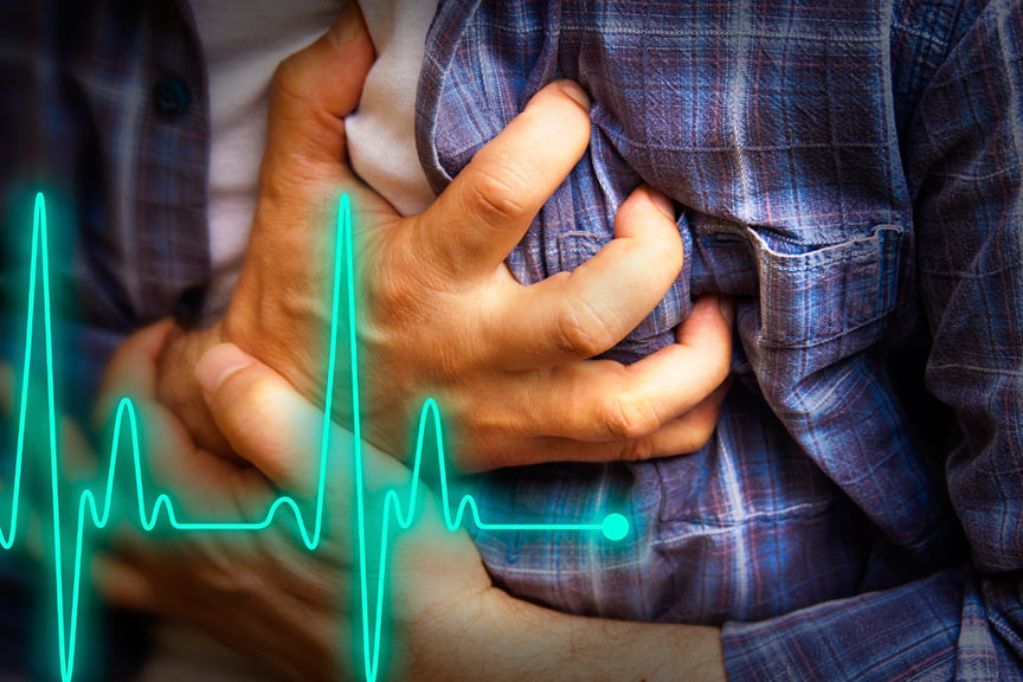
Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart, and it’s a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina pain is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness, or pain in the chest.
Symptoms:
Angina symptoms include chest pain and discomfort. The chest pain or discomfort may feel like:
– Burning
– Fullness
– Pressure
– Squeezing
Pain may also be felt in the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back.
Other symptoms of angina include:
– Dizziness
– Fatigue
– Nausea
– Shortness of breath
– Sweating
Causes:
The most common cause of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle is coronary artery disease (CAD). The heart (coronary) arteries can become narrowed by fatty deposits called plaques. This is called atherosclerosis.
Risk factors:
Increasing age. – Angina is most common in adults aged 60 and older.
– Family history of heart disease.
– Smoking, alcohol, and drugs.
– Diabetes.
– High blood pressure.
– High cholesterol or triglycerides.
– Obesity and not enough exercise.
Emotional stress and hormonal imbalance.
– Anxiety.
– Cold temperatures.
When to see a doctor:
If your chest pain lasts more than a few minutes and doesn’t go away with rest or with angina medication, this could be a sign that you are having a heart attack.
If chest discomfort is a new symptom for you, it’s important that you see a doctor to determine the cause and get treatment.
Prevention:
You can help prevent angina by following the same lifestyle changes that are used to treat angina. These include:
– Not smoking.
– Eating a healthy diet.
– Avoiding alcohol.
– Exercising regularly.
– Maintaining a healthy weight.
– Managing other health conditions related to heart disease.
– Reducing stress.
– Getting recommended vaccines to avoid heart complications.